FCOMI Flags: FP Compare and store status in EFLAGS +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ +----------+----------+ |O|D|I|T|S|Z|A|P|C| | 11011p11 | 111uuiii | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ +----------+----------+ | | | | | | | | | | | Dn | xx | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ +----------+----------+
FCOMI ST, STi
p=0
DB F0 + i FCOMI ST, Sti ; Compare and move results to Integer flags
DB E8 + i FUCOMI ST, Sti ; Unordered compare, move results to Int. flags
p=1
DF F0 + i FCOMIP ST, Sti ; Like FCOMI, and Pop FP stack
DF E8 + i FUCOMIP ST, Sti ; Like FUCOMI, and Pop FP stack
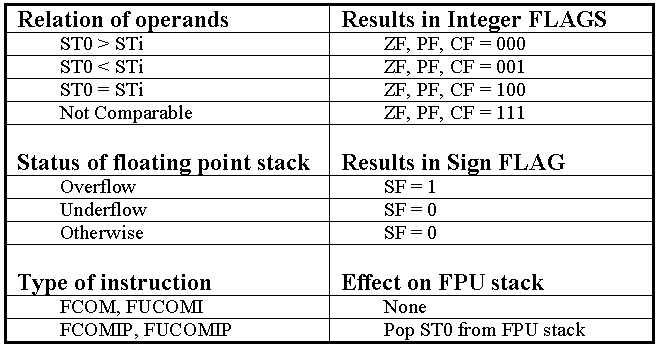
The algorithm for FCOMI is best summed up by a table, not pseudo-code. Table 1 describes the behavior of FCOMI.
Table 1 -- Behavior of FCOMI instruction

This instruction will compare Sti against the stack top, and store the results in the Integer FLAGS (EFLAGS) register. The usefulness of this instruction lies in the number of instructions saved to store the FP status word (FSTSW) into AX, then load AH into EFLAGS (SAHF). This means that immediately following this instruction, a conditional jump instruction may be executed based on the results of the comparison.
Normally, no FPU flags are affected by FCOMI. However, if an exception occurs, then the FPU flags are affected as follows:
FSW.C1 will be set to indicate a stack underflow or overflow condition (U/O#).
The FCOMI opcodes are newly defined for P6, however don't always produce an invalid opcode exception (#UD) on previous x86 processors. The encodings for FCOMI produce an invalid opcode exception on the Pentium and Intel486 processors, but are ignored, and treated like an FNOP by the Intel387 math coprocessor. Behavior for the 8087 and 80287 math coprocessors is undefined.
If either operand to FCOMI or FUCOMIP is a NaN, is in an undefined format, or if a stack fault occurs, an invalid operand exception occurs, and the FPU flags are set to "unordered."
If either operand to FUCOMI or FUCOMIP is an SNaN, is in an undefined format, or if a stack fault occurs, and invlid operand exception occurs, and the FPU falgs are set to "unordered."
If either operand to FUCOMI or FUCOMIP is a QNaN, the FPU flags are set to "unordered." Whereas FCOMI and FCOMIP raise an invalid operand exception, FUCOMI and FUCOMIP do not. This behavior only occurs for a QNaN operand.
For all FCOMI instruction variants, the size of zero is ignored (-0.0 = +0.0).
D, I, IS
Exception 7 (#NM) if EM or TS is set in CR0.
Exception 7 (#NM) if EM or TS is set in CR0.
Exception 7 (#NM) if EM or TS is set in CR0.
The first example shows a normal stream of instructions which would be used to perform a conditional move in an Intel386-compatible manner. The second example replaces this code with use of the FCOMI instruction. A more powerful example can be seen when FCOMI is combined with FCMOV instruction.
FCOM ST0, ST1 ; Floating point compare
FNSTSW AX ; Store floating point flags in AX (no wait)
SAHF ; Move AH to integer flags register
Jcc Continue ; Branch on some condition
... ; do many instructions in this code block
Continue:
FCOMI ST0, ST1 ; Floating point compare
Jcc Continue ; Branch on some condition
... ; do many instructions in this code block
Continue:
Get description of [AAM] [AAD] [UMOV] [LOADALL]
New P6 OpCodes [CMOV] [FCMOV] [RDPMC]
[INT01] [SALC] [UD2]